What Was Primary Subject Matter of Ancient Chinease Art
China is ane of the largest countries in the earth, it spans roughly over 9000 square kilometers and is populated by over ane.4 billion people. China is a big and vast land, which too means it has a rich history and culture. This article will explore various facts well-nigh Chinese fine art and civilization.
Table of Contents
- 1 A Historical Overview of China
- 1.1 The Beginnings of Prc: The Neolithic Age
- 1.two A Brief Overview of the Chinese Dynasties
- 2 What Is Chinese Art?
- 2.1 Characteristics of Chinese Art
- 2.two Types of Chinese Art
- 3 Chinese Art: Then and At present
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 When Did Chinese Art Beginning Occur?
- 4.ii What Are Some of the Main Forms of Chinese Fine art?
- four.3 What Are the Characteristics of Chinese Art?
- 4.four What Was Chinese Painting?
A Historical Overview of Cathay
Chinese art history goes back to its prehistoric roots in ancient China artwork. For us to accept a better understanding of ancient Chinese fine art nosotros volition provide a brief historical overview starting from the Neolithic menses all the way through the numerous Dynasties that shaped not merely Chinese politics and order, only the Chinese art culture.
The Ancestry of Communist china: The Neolithic Age
When we look at the history of China, it dates to early prehistoric times (over two meg years) when the fossils from what is referred to every bit the Peking Homo, or Homo erectus pekinensis, were found in northern China in the Zhoukoudian Cave, which is in the Fangshan District in Beijing.
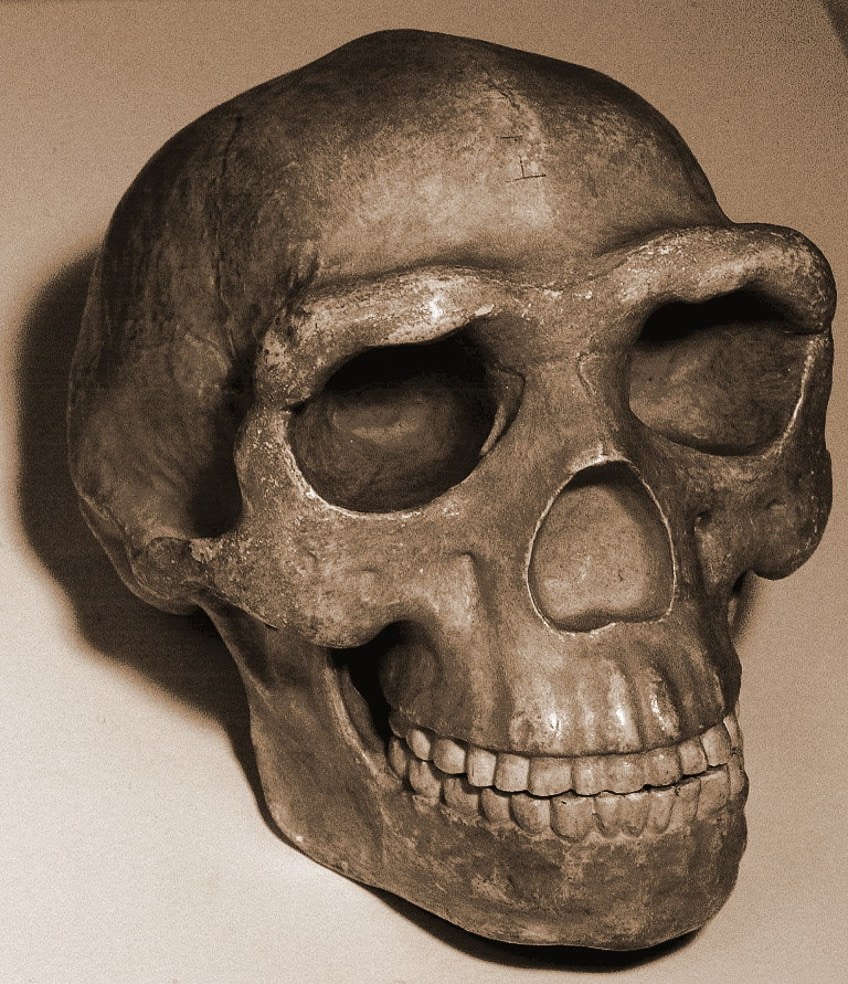 The skull of the Peking Human; kevinzim, CC Past ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The skull of the Peking Human; kevinzim, CC Past ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) in China is also dated effectually 7000 BCE to 1700 BCE with diverse cultures that were mainly hunting and farming communities. They developed in other areas of community life, for example, building homes, using various tools, domestication of animals, as well every bit the product of pottery, which is a significant aspect of ancient Mainland china artwork.
A Brief Overview of the Chinese Dynasties
The first political and economic arrangement in China's history is said to take started when the first dynasties, or monarchies, were established. In total, at that place were 83 dynasties with over 500 emperors during People's republic of china'south Majestic history.
Many sources state that it started with the Xia Dynasty around 2070 to 1600 BC, ruled by the emperor Yu the Great.
However, at that place is also minimal evidence left behind that tin can verify this dynasty's existence and it has been described every bit a "mythical" dynasty. Furthermore, sources country it was invented by the Zhou Dynasty that ruled afterward the Shang Dynasty, which succeeded Xia (for simplification, it was the Xia Dynasty, then the Shang Dynasty, and then the Zhou Dynasty, only we will explore these further beneath).
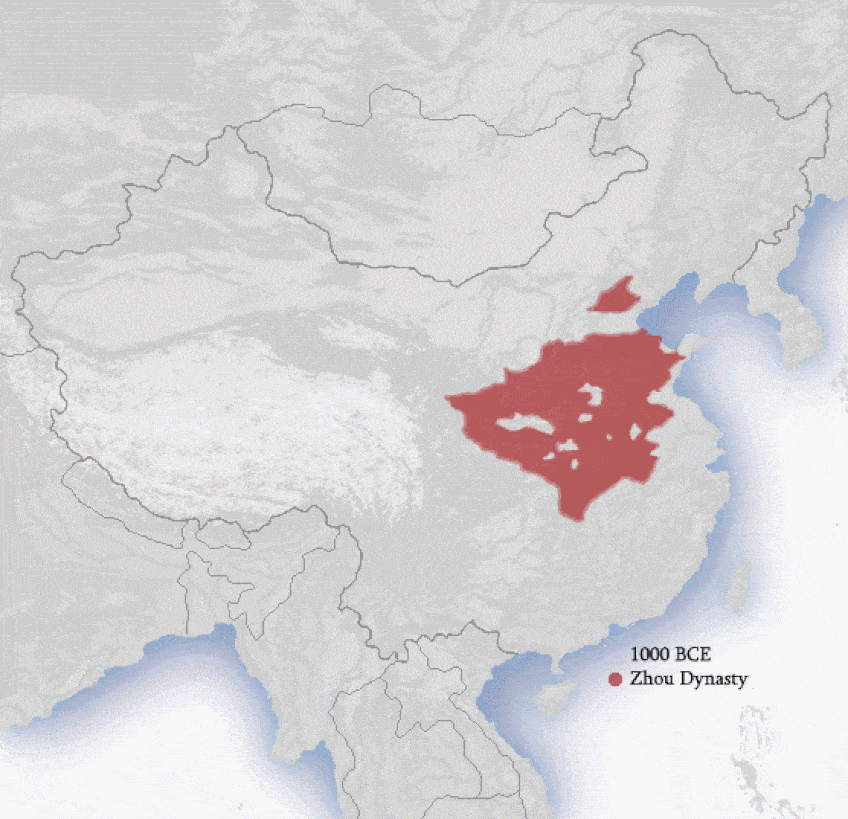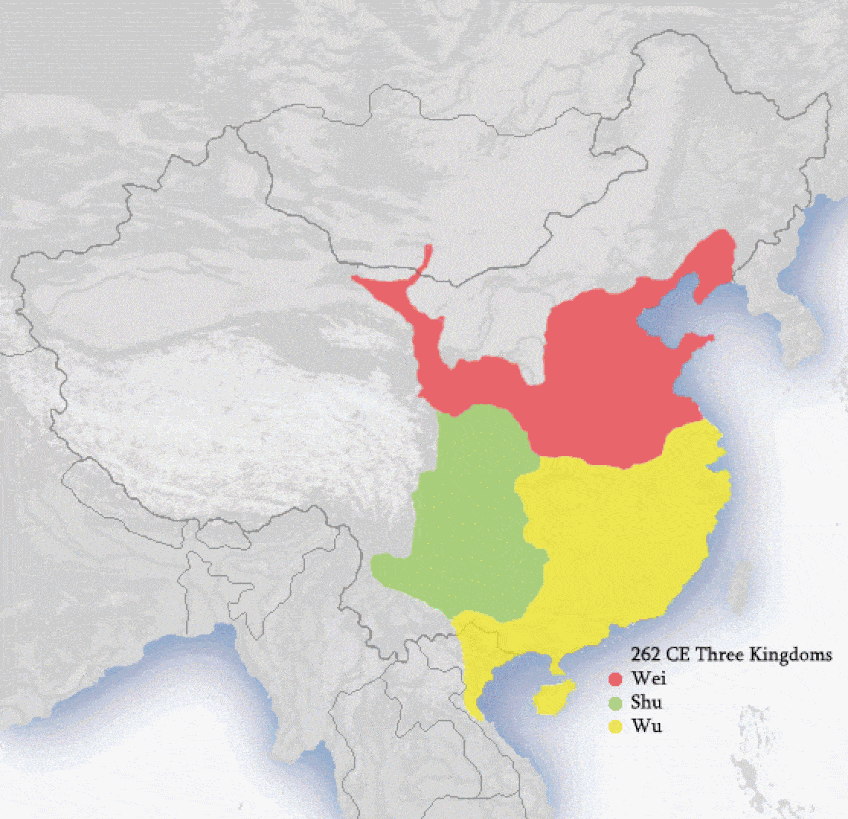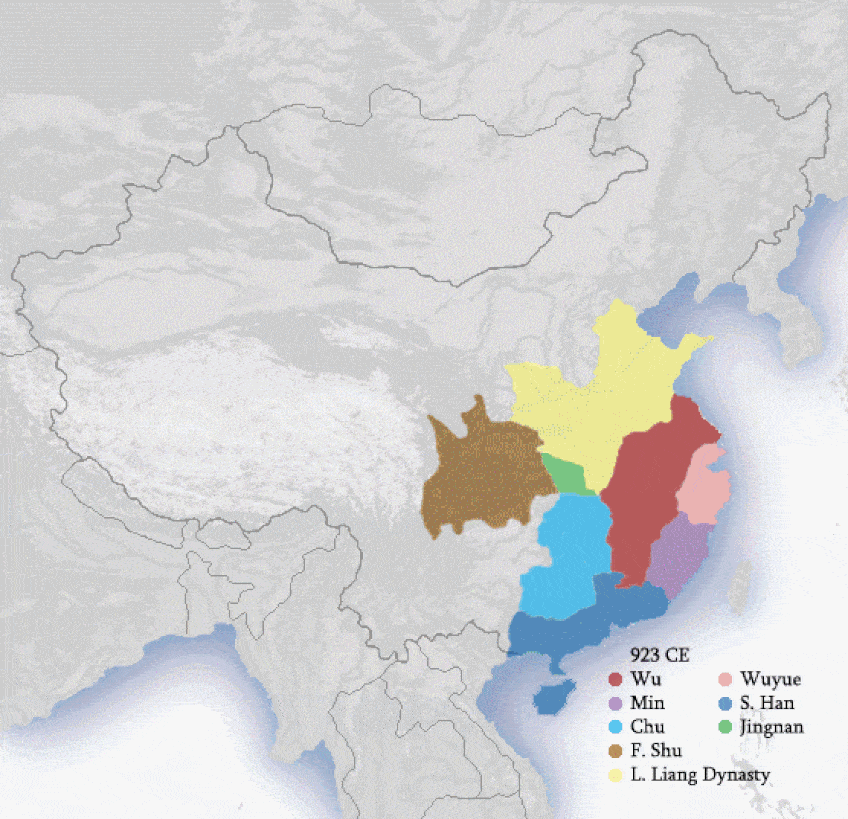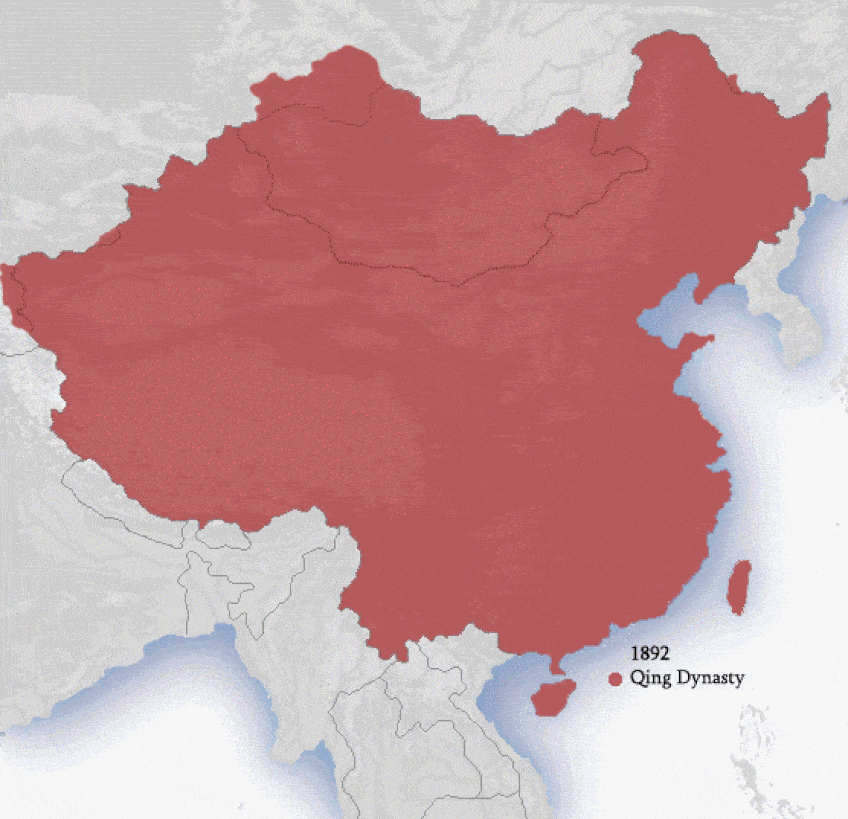 The approximate territories of dynasties in China. Drawn by Ian Kiu;Pojanji, CC Past-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The approximate territories of dynasties in China. Drawn by Ian Kiu;Pojanji, CC Past-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Shang Dynasty (also known as the Yin Dynasty) ruled from 1600 to 1046 BCE with its roots in the Yellow River Valley. From various excavations, this dynasty'south existence has been verified as factual. The Yellow River is believed to exist the 2nd-longest river in Prc and was the originating source or "cradle" of the Chinese civilization. This historic period was marked by numerous advancements like writing, astronomy, maths, and what is sometimes understood as the "Early Bronze Age".
The Zhou Dynasty ruled from around 1050 to 221 BCE, and they shared a lot of similarities with the previous Shang Dynasty. This menstruum is besides marked as being the "Late Bronze Historic period" of China. Some other important political tool utilized and enforced during this period was the Mandate of Sky. This was really a philosophy and belief organisation that Heaven (Tian) decided when a ruler would exist overthrown and succeeded by the next rightful ruler.
During this fourth dimension, the philosophies of Confucius and Laozi also developed, respectively, Confucianism and Taoism. These philosophies became worldwide ways of thought, and are nonetheless present today.
The Zhou Dynasty ruled over 700 years and was ane of the longest-ruling dynasties in ancient China's history. Information technology ended due to ensuing wars and conflict between the individual states and when the Male monarch was forced to flee to the eastern upper-case letter, Luoyi, the Eastern Zhou Dynasty developed (this was during 771 to 221 BCE). This period was further marked by the first half called the Spring and Autumn Period and the latter one-half called the Warring States Menstruum (475 to 221 BCE).
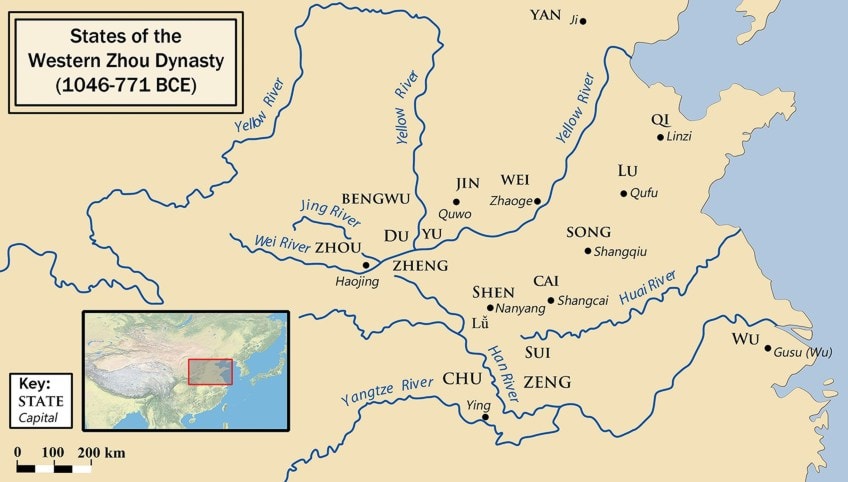 States of the Western Zhou Dynasty (1046-771 BC);Philg88, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
States of the Western Zhou Dynasty (1046-771 BC);Philg88, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Qin Dynasty (221 to 206 BCE) developed from the conflicts during the Warring States flow with King Zheng of Qin as the first emperor. The Qin Dynasty ruled for simply a brusque period of time and ushered in new systems that organized the state and laid foundations that became the construction of the Chinese government. This was also the first regal dynasty in China.
What was different about the Qin Dynasty was that it was centralized, with the ruling power beingness united compared to the previous powers dispersed among the different states that eventually warred with ane some other for power (as mentioned above).
The Qin Dynasty vicious afterward the decease of the showtime emperor and the strife of civil state of war, the beginnings of the succeeding Han Dynasty (206 BCE to 220 CE) developed.
The Han Dynasty was ruled past Liu Blindside, otherwise Emperor Gaozu of Han, and as the second regal dynasty introduced many new developments in China. It was marked equally a period of flourishing growth in various aspects, economically, every bit well as establishing new trade routes like the Silk Road, which reached as far as the Mediterranean.
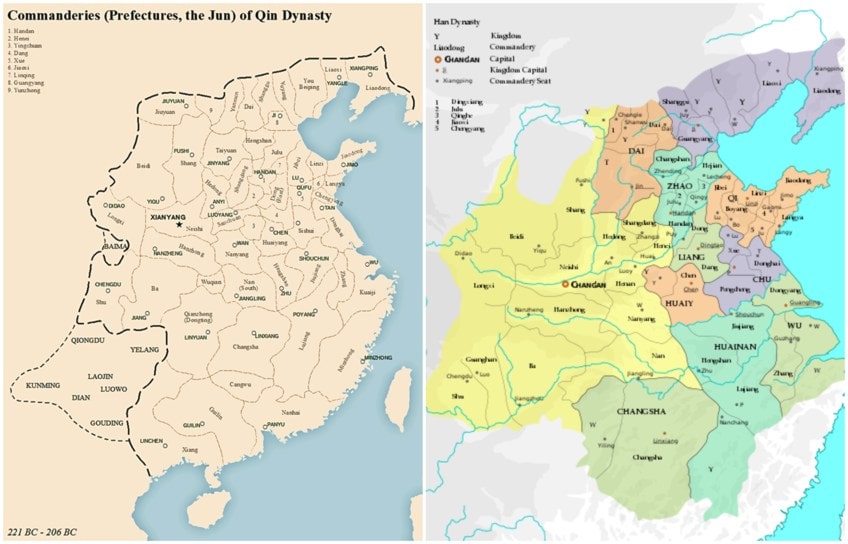 LEFT: Map of Qin Dynasty and its administrative divisions; SY, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | RIGHT: Kingdoms and commanderies of Han dynasty in 195 BC; Esiymbro, CC Past-SA four.0, via Wikimedia Commons
LEFT: Map of Qin Dynasty and its administrative divisions; SY, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | RIGHT: Kingdoms and commanderies of Han dynasty in 195 BC; Esiymbro, CC Past-SA four.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Han Dynasty was divided into the Western Han (202 BCE to 9 CE) and the Eastern Han (25 to 220 CE). There were over 20 emperors during this period with Emperor Wu being one of the longest to rule (over l years). When the Han Dynasty roughshod, in that location was a time of division between the states during the years 220 to 589 CE. This became known as the Three Kingdom period, ruled past the three states, Wu, Wei, and Shu.
The period of division lasted around 400 years and was only reunified again past the Sui Dynasty (581 to 618 CE).
The Sui Dynasty was a short menses, succeeded by the Tang Dynasty (618 to 907 CE). The other dynasties that followed were, namely, Song Dynasty (960 to 1279 CE), the Yuan Dynasty (1271 to 1368 CE), the Ming Dynasty (1368 to 1644 CE), the Qing Dynasty (1644 to 1911/12 CE), and then what marks China as the Modernistic period, from 1912 to the nowadays day. The Republic of Mainland china was founded in 1912.
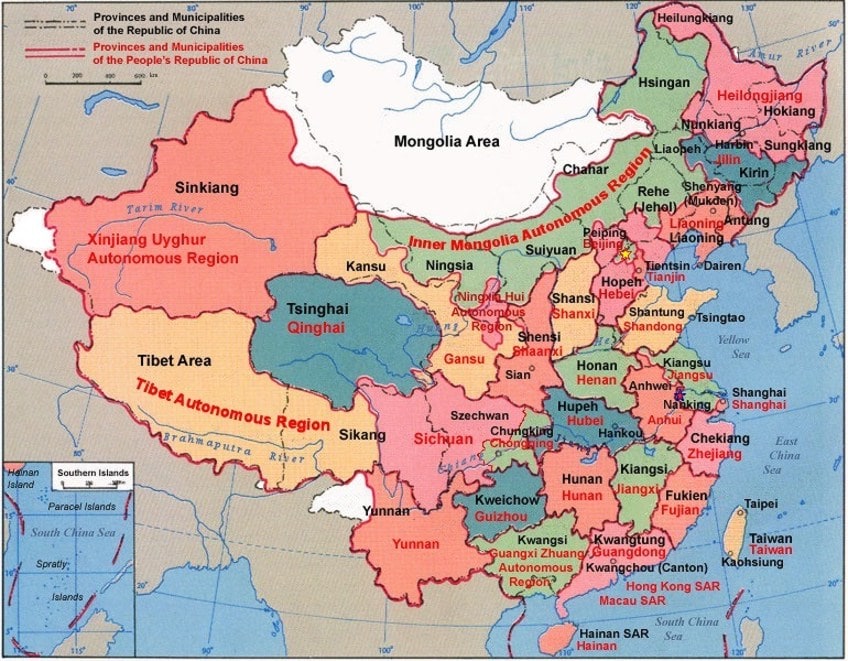 Comparison betwixt Commonwealth of People's republic of china and People's Republic of Red china authoritative divisions;Electionworld, CC By-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Comparison betwixt Commonwealth of People's republic of china and People's Republic of Red china authoritative divisions;Electionworld, CC By-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
During all the purple periods, there were significant changes to the evolution of China and periods of war and conflict that divided the states and reunified them over again nether imperial rule. The menses of the partitioning after the Han Dynasty is when the influence of the Buddhist religion developed and spread with many temples being built.
The Tang Dynasty, for example, was marked every bit a Gold Age during Communist china's history with improved economic and military structures as well as a flourishing civilisation.
The Silk Route became a prosperous merchandise route that allowed cultures to exchange various goods similar textiles, metals, and drinking glass. This further developed and encouraged the creation of Chinese artwork in the form of pottery (ceramics) and painting.
What Is Chinese Fine art?
Chinese fine art history encompasses all the visual arts originating in People's republic of china and produced by the Chinese cultures and artists. It is marked past many unlike types, ranging from Neolithic pottery to calligraphy, painting, verse, porcelain, statuary work, jade carving, and many others. Information technology begins from the Prehistoric historic period upwards to the nowadays, Contemporary age. Traditional Chinese art shares commonalities, withal, it was also produced differently inside each dynasty, which are central distinguishing periods marking the progression of Chinese artwork.
Below, nosotros will discuss some of the cardinal characteristics underpinning Chinese artwork, every bit well equally take a closer look at significant Chinese art through different modalities.
Characteristics of Chinese Art
The common underpinning characteristics that give Chinese art its nature come from philosophical, religious, and cultural beliefs. Chinese culture has always valued nature and its inherent significance. We will find that a wide multifariousness of subject matter is ofttimes of natural elements, for case, foliage and plants similar bamboo, flowers, animal life-like birds, equally well as mural depictions.
 Symbols used in ancient Chinese art, from Decorative textiles; an illustrated book on coverings for piece of furniture, walls and floors, including damasks, brocades and velvets, tapestries, laces, embroideries, chintzes, cretonnes, drapery and piece of furniture trimmings, wall papers, carpets and rugs, tooled and illuminated leathers (1918);Net Annal Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
Symbols used in ancient Chinese art, from Decorative textiles; an illustrated book on coverings for piece of furniture, walls and floors, including damasks, brocades and velvets, tapestries, laces, embroideries, chintzes, cretonnes, drapery and piece of furniture trimmings, wall papers, carpets and rugs, tooled and illuminated leathers (1918);Net Annal Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
This inherent significance of nature revolved around a deeper belief in the spiritual aspects of life and the external world being a "manifestation" of that. Artists sought to depict the deeper meanings of life and the universe. This also ties in with the stiff moral and upstanding beliefs many artists had.
Calligraphy and landscape painting were two of the most important types (or "highest forms") of Chinese artwork. Mural painting would depict more ideal scenes of nature, sometimes these were non a true-to-nature reflection of the actual landscape.
For example, depictions of mountains would stand for the thought of heaven as they motion upward towards college aspects of nature and, ultimately, the spiritual. Other depictions would be to inspire people who looked at the artwork.
Chinese artists were followers of Confucianism, and their moral standpoints were reflected in their art. Chinese artwork sometimes appears simpler and more minimal in its depictions without the need to be bashful or overzealous almost the creative person's talents or skills every bit an artist. Chinese artwork would often reflect the moral character of the artists themselves.
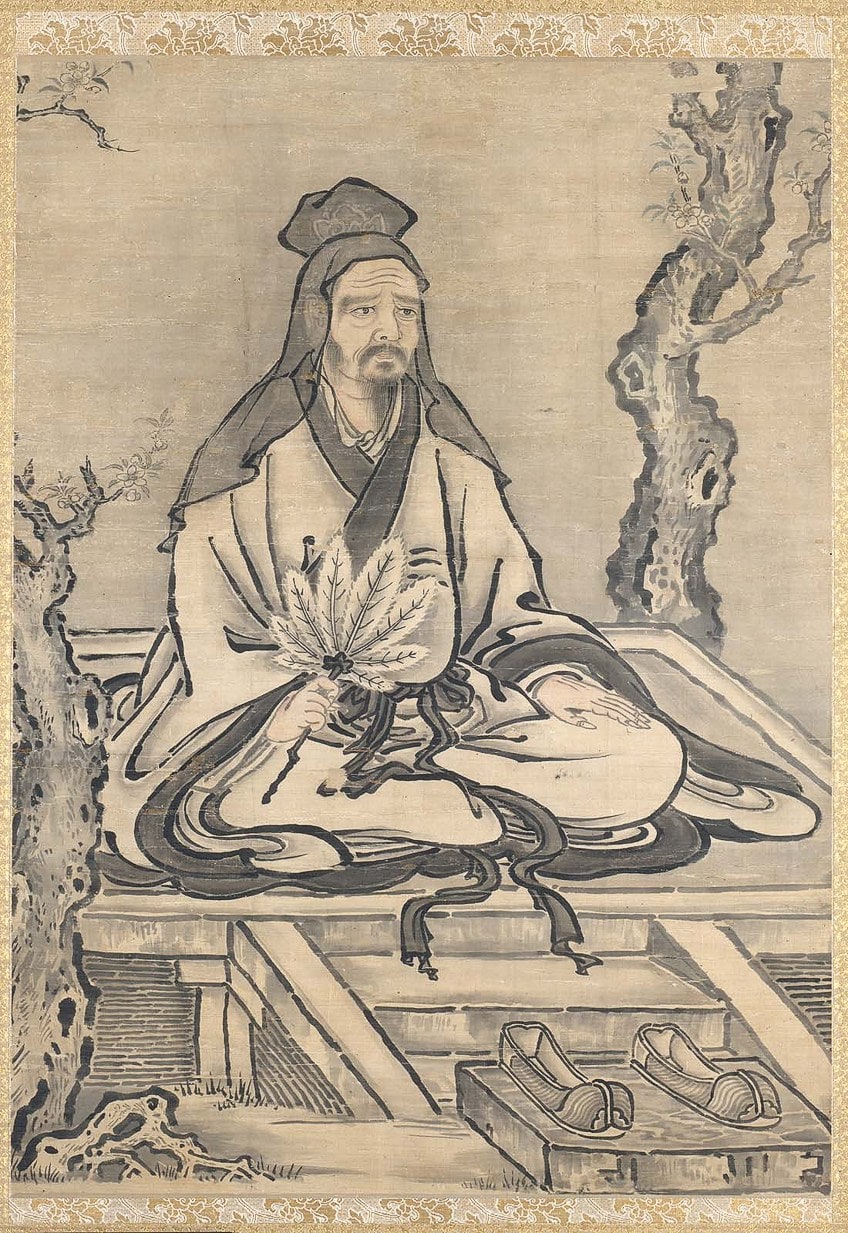 Confucious in Confucius and His Disciples Yanzi and Huizi at the "Apricot Altar" (mid-17th century) by Kano Tan'yû (1602–1674);Kano Tan'yû (1602–1674), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Confucious in Confucius and His Disciples Yanzi and Huizi at the "Apricot Altar" (mid-17th century) by Kano Tan'yû (1602–1674);Kano Tan'yû (1602–1674), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Another important point about Chinese painters and calligraphers is that most artists also had a stiff scholarly groundwork, in fact, information technology became a prerequisite to have cognition of other artistic masters to be an creative person.
Courtroom art was some other attribute of Chinese artwork, artists would frequently exist commissioned by the patron or the Majestic court. This type of artwork would human activity every bit decoration for the interior of their palaces, various buildings, and tombs.
Types of Chinese Fine art
At that place were many contributing factors surrounding Chinese artwork and it is important to remember the evolution of these modalities throughout the unlike developments of each Dynasty and periods of conflict. Some modalities served dissimilar purposes and meanings.
As the ages progressed, artists would utilize unlike media and surfaces too.
Chinese Painting
Nosotros have what is known in Chinese, wenfang sibao, or "Four Treasures of a Scholar's Studio" – this was an of import function of Chinese painters' and calligraphers' skills and toolsets. It consisted of newspaper, brushes, ink, and inkstone. It is said to accept originated during 420 to 589 CE, during the Southern and Northern Dynasties.
All the same, the paintbrush as an creative tool in Chinese art culture is believed to date all the way dorsum to the Neolithic flow and was utilized and considered every bit a creative tool during 476 to 221 BC, which is the time of the "Warring States" in Chinese history.
The mode the paintbrush was made ordinarily consisted of animal hair for the bristles, which would come from unlike animals giving varying degrees of thickness. This would and so exist attached to a stick, which would commonly be bamboo.
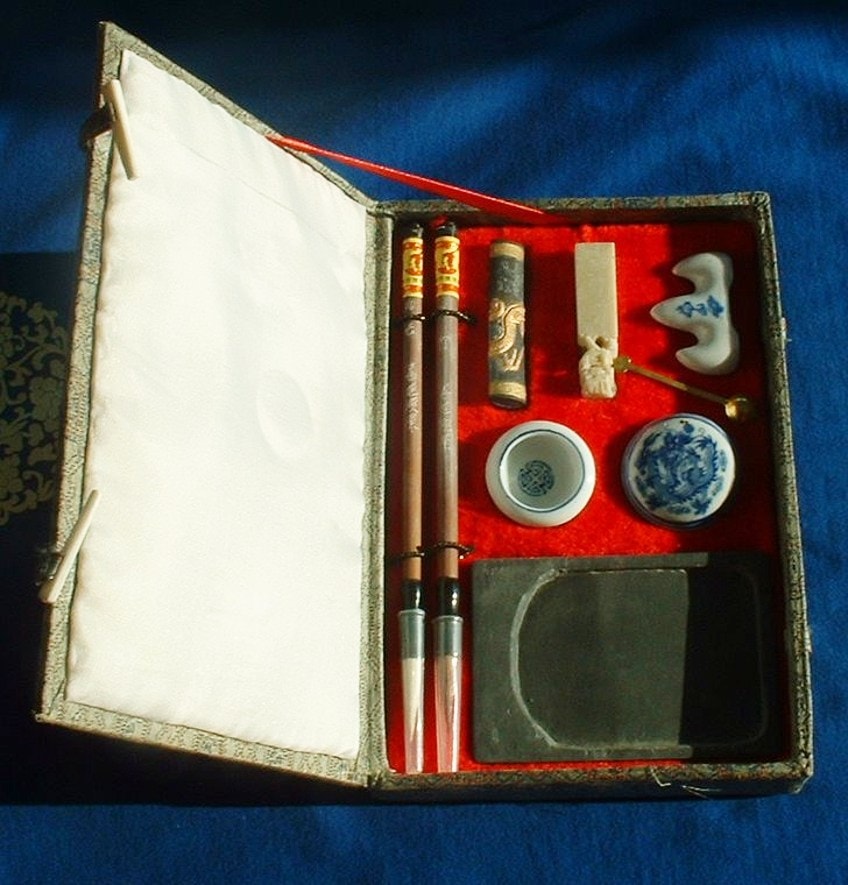 The Four Treasures of Chinese calligraphy;Immanuel Giel, CC Past-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Four Treasures of Chinese calligraphy;Immanuel Giel, CC Past-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Paintings were usually created on newspaper, which would then be mounted on silk. At that place were different types of ways paintings would exist mounted, for instance, scrolls in the form of hand or hanging scrolls, fans, leaves done as album leaves, amid others.
Hanging scrolls were vertical in shape and supported by wooden rods and strips as weights for the painting to be hung on a cord and stay open.
They were also able to fold upward easily. Handscrolls were also usually rolled upward and taken out to exist viewed on special occasions. These would exist viewed from right to left, every bit it is unrolled the various scenes would appear and viewers would take function in this as a ceremonial human action.
An example is a hanging whorl simply titled, Mountain Landscape (c. 1600s), from the Ming Dynasty past Dong Qichang. Information technology is 95.five by 41 centimeters in size depicting a mountainous landscape with diverse vegetation. The painting is equanimous in a manner where our eyes, as the viewers, are guided to move in an upwards direction towards the top tip of the mountain in the groundwork (near the upper part of the hanging coil). We also notice how the creative person created depth to the painting by highlighting areas with darker shades of ink.
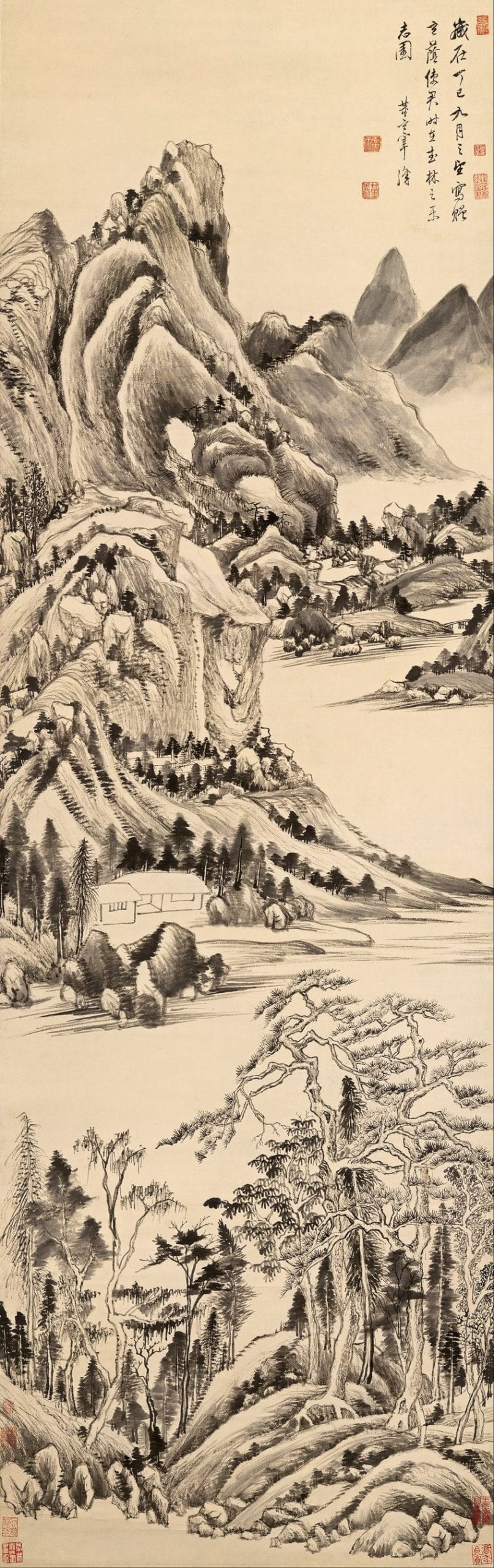 Mountain Landscape (c. 1617) by Dong Qichang, Ming Dynasty; Dong Qichang, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Mountain Landscape (c. 1617) by Dong Qichang, Ming Dynasty; Dong Qichang, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
An example of a handscroll painting is from the afterward 1900s by Zhu Xiuli who repurposes a traditional Chinese art in his handscroll titled, Landscape (1985 to 1989). This is a reproduction of what we will see in traditional handscrolls. It depicts a mural with houses and varying types of copse hither and there. The image is depicted with smooth lines and dynamic fluidity.
Other forms of Chinese painting include fans, for case, Landscape in the Style of Yan Wengui (c. 1707) by Wang Hui, which was painted in the manner of famous tenth-century painter Yan Wengui, and depicts classical mural every bit a subject area matter. We notice several trees to the left with a pavilion area to the correct-mitt side of the composition. At that place are as well the feature ink markings that delineate the mountains in the groundwork, and furthermore, the ink markings are horizontal and vertical in shape.
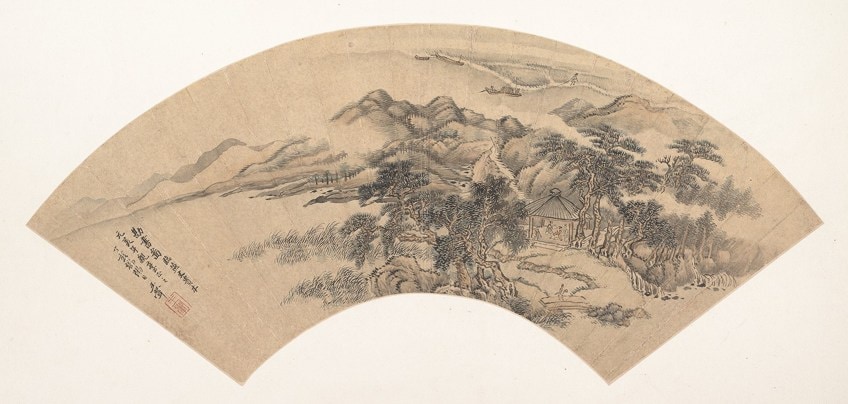 Landscape in the Fashion of Yan Wengui (c. 1707) past Wang Hui;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Landscape in the Fashion of Yan Wengui (c. 1707) past Wang Hui;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Side by side to the images, we also notice various calligraphic inscriptions decorating the middle left part of the fan, which are reported to be washed by other artists aslope Wang Hui. Wang Hui was role of several other painters, the group was chosen the "Four Wangs", who were from the Qing Dynasty period from 1644 to 1911.
Fans were unremarkably made to exist given as gifts with the typical landscape painting as its bailiwick affair.
Similarly, there would also be inscriptions on the fans like the in a higher place-mentioned fan. The inscriptions would oftentimes vary every bit comments and notes from peers. There were also unlike types of fans, for example, some were made of stiffened silk and the other would be fabricated of paper. These would exist mounted between bamboo sticks as support.
Other examples of landscape paintings from one of the famous artists, Fan Kuan, who painted during the Vocal Dynasty from 960 to 1279 CE. Kuan is well known for his landscape paintings of mountains and the natural environments that he was inevitably inspired by. Many sources virtually him state that he lived as a recluse, away from the politics of conflict from what was the "V Dynasties" period.
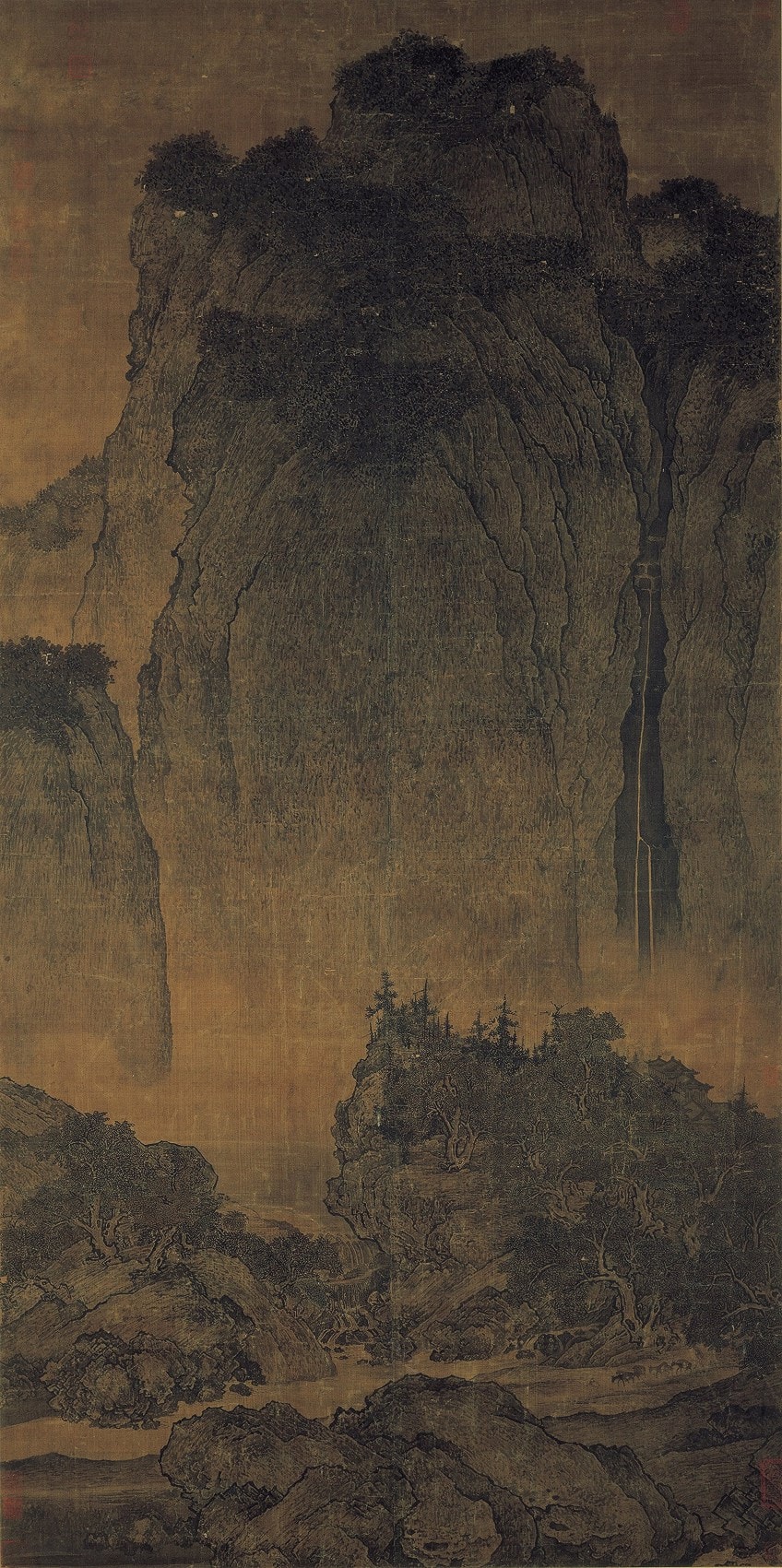 Travelers by Streams and Mountains (c. yard) by Fan Kuan;Fan Kuan, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Travelers by Streams and Mountains (c. yard) by Fan Kuan;Fan Kuan, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
In his work titled, Travelers by Streams and Mountains (c. 1000 CE), there is an element of depicting the search for truth. The artist was also influenced by Neo-Confucian thought at the time, which revered a sense of truth that came from the natural earth. The higher up-mentioned painting, which is in the format of a hanging scroll around seven feet high.
The composition is divided into three aspects, namely, the large boulders in the foreground, the opening in the centre of the painting with various trees and outgrowths of foliage, and the background growing into alpine mountains with its tips topped with bushy-similar foliage.
There are various other details within this painting, which emphasize the calibration of the mountains compared to the minute details.
For example, the men and donkeys in the bottom right corner, including the temple hidden between the trees. The calibration of the figures confronting the scale of the towering mountains suggests the sheer vastness of Kuan's landscape and its majestic qualities.
Nosotros will detect fifty-fifty more skill in the creative person's techniques to return the subject thing in every bit much detail every bit possible. At that place are varying degrees of thickness in the brushstrokes, we run across this so delicately done in the mountain crevices. Additionally, the artist too utilized ink wash and dots to create the depiction of texture.
Another example is titled, Appreciating Potted Chrysanthemum in Serenity past Ming dynasty artist Shen Zhou. This painting depicts a mural with a gazebo standing to the far right of the horizontal limerick.
 Affectionate Potted Chrysanthemum in Tranquility (Ming Dynasty) past Shen Zhou; Public Domain, Link
Affectionate Potted Chrysanthemum in Tranquility (Ming Dynasty) past Shen Zhou; Public Domain, Link
There are four figures beneath the awning, three of whom are sitting at a table and the fourth figure standing to the left holding a jug of sorts. Behind the awning is a row of potted chrysanthemums. The remainder of the landscape is filled with trees.
Nosotros volition also notice the characteristic calligraphic inscriptions to the left of the painting, which are poems.
The painting, Eleven Dragons (c. fifteenthursday Century), by Chen Rong of the Ming Dynasty period is another handscroll, which depicts eleven dragons along with the 16-pes-long scroll. The dragons are all depicted dynamically on mount cliffs and clouds.
The colour of the dragons is monochromatic ink along with detailed lines delineating the forms and shapes. Dragons take been powerful symbols throughout ancient Chinese fine art and symbolize various qualities of strength similar masculinity besides every bit attributes to imperial power or royalty and wisdom.
Chinese Pottery
Chinese pottery goes dorsum all the way to the prehistoric period when information technology was utilized for utilitarian purposes as well equally for burying purposes as many accept been excavated from burial sites, known besides as funerary jars. Chinese pottery has been throughout the ages, developing into many dissimilar styles and forms equally traditional Chinese art. Neolithic pottery was besides painted and decorated by etching bands of patterns into course.
Chinese pottery also spans ceramics and porcelain. When nosotros look at Chinese porcelain, nosotros will find there is a vast array of delicately decorated pieces, a testament to the inherent creative skill of this blazon of Chinese artwork.
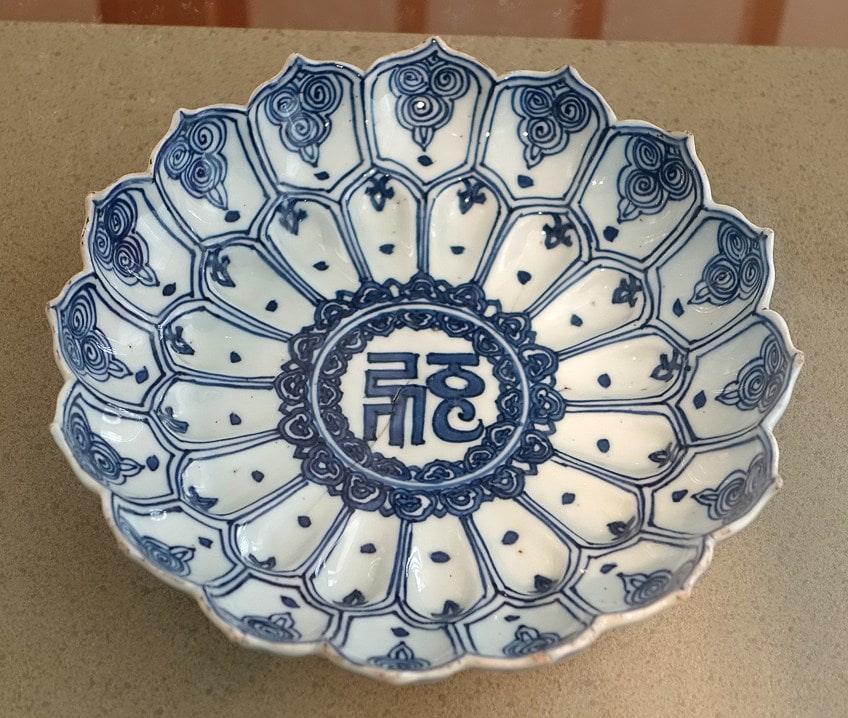 Bluish and white porcelain dish in the form of a lotus lily with Sanskrit script. Jingdezhen, China, Ming dynasty, Wanli period, 1573-1619;Daderot, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Bluish and white porcelain dish in the form of a lotus lily with Sanskrit script. Jingdezhen, China, Ming dynasty, Wanli period, 1573-1619;Daderot, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Blue and white porcelain was prevalent in People's republic of china during the 1300s and was utilized in temples, these were also a widely made form of porcelain with a blue underglaze instead of a blood-red underglaze. The red underglaze was also produced during the Yuan Dynasty (1279 to 1368 CE).
When we wait at some of the examples, we will detect diverse designs and patterns on unlike types of vessels. The Blue and White Porcelain Jug (c. early xvth Century), from the Ming Dynasty, depicts floral patterns painted on most of the jug. The jug has a large belly, which tapers into a wider neck and opening (it is believed the jug as well had a lid).
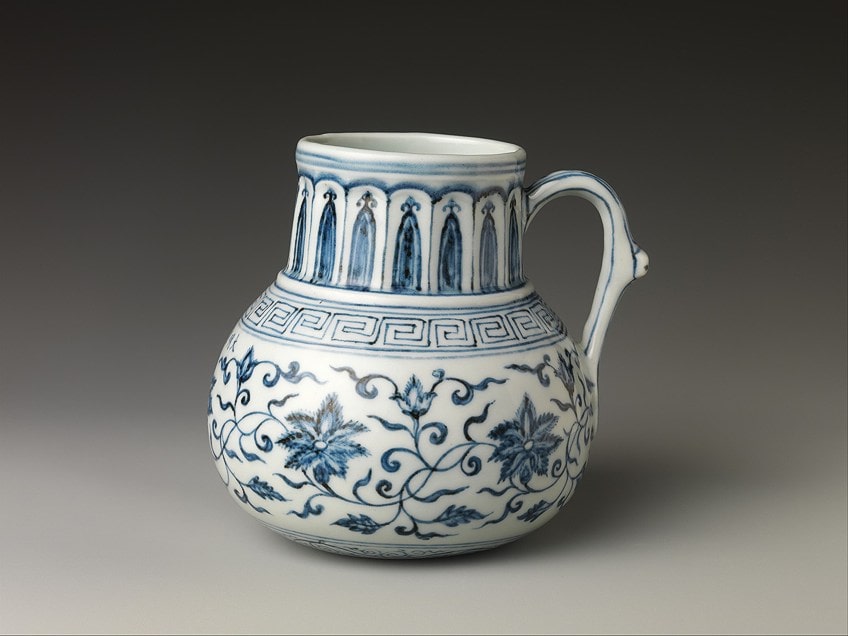 Blueish and White Porcelain Jug, 15th century, Ming Dynasty;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Blueish and White Porcelain Jug, 15th century, Ming Dynasty;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Chinese art history almost does non seem complete without mentioning the famous Terracotta Army warriors from the tomb of the first Chinese emperor during the Qin Dynasty (c. 210 BCE) – masterpieces of Chinese sculpting to this twenty-four hour period. The warriors were found in Lintong Canton in the Shaanxi Province during 1974 in "pits" or underground chambers that were dug up by farmers.
They were discovered as diverse terracotta fragments, which turned out to exist an entire army of terracotta warriors made to protect the tomb (mausoleum) of the Qin Emperor.
The figures were all varied in their size and stature and there were also horses, chariots, and an assortment of other figures like musicians and strongmen, which were believed to be entertainers for the emperor in the afterlife. Some of the more than important figures similar generals were sculpted every bit taller than other figures that were warriors. In other words, the size would indicate the "role".
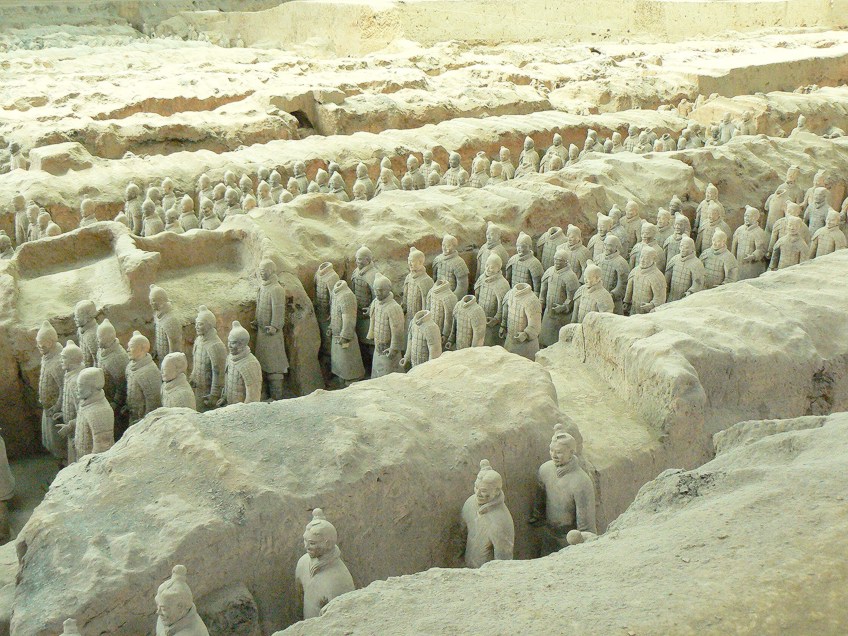 Terracotta Army warriors, Qin Dynasty, c. 210 BCE; Will Clayton from Blackburn, United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland, CC BY ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Terracotta Army warriors, Qin Dynasty, c. 210 BCE; Will Clayton from Blackburn, United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland, CC BY ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The terra cotta warriors requite us some interesting facts virtually Chinese fine art, it is indicated that there were effectually 8, 000 figures of soldiers with sources reporting that even more figures take been found, over 100 chariots, and over 600 horses.
Not only is this one of the largest archaeological finds in history, only information technology is also considered the eighth wonder of the world.
The creation of this vast terra cotta army is estimated to have taken effectually forty years to consummate with around 700 000 people who worked towards its completion. The detail of each terra cotta effigy is another attestation to the skill of aboriginal Chinese fine art and Chinese sculpting. When we expect at each figure, we will find that each one is individualized and sculpted in fine detail, from facial features to clothing. When they were discovered, some terracotta figures still had remnants of color from the paint that was on them.
Other Chinese Artworks
Aboriginal Chinese art is not express to but calligraphy and painting, there are multitudes of other fine art forms inside the history of Chinese arts. Some notable modalities also include Chinese ritual bronzes, which were made as part of graves. There is a meaning collection of these bronzes all made with incredible skill and craftsmanship.
The bronzes were likewise made in different shapes and forms, for example, some were in the shape of different animals.
Apart from the primary utilization for ritual, bronzes were as well made for other reasons. It is reported that during the Vocal Dynasty bronzes were fabricated for different reasons, such as vessels for water, wine, food, cede, measurements, weapon containers, musical instruments, and others.
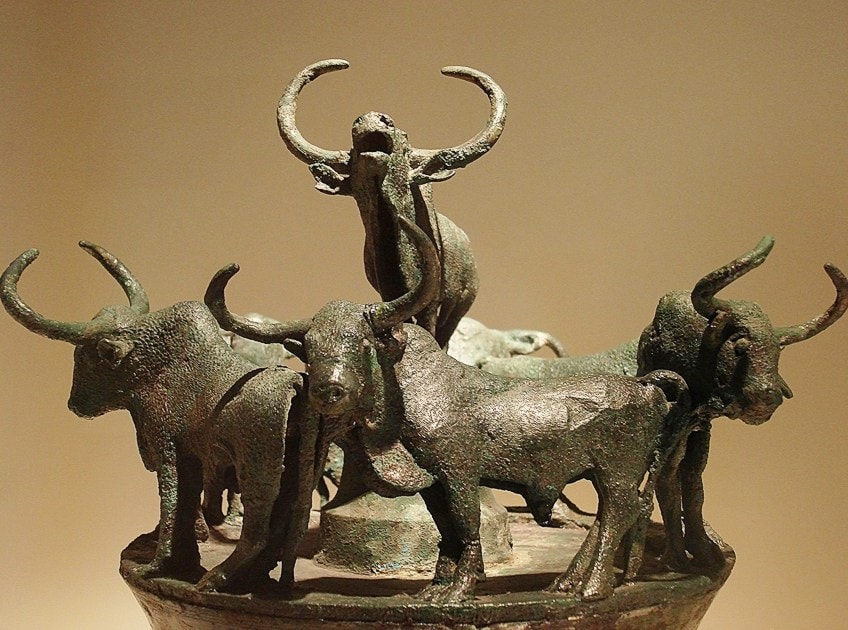 Statuary Cowrie Container, Western Han Dynasty (206 B.C. – A.D. 8). Excavated at Jinning, Yunan Province, 1956; Editor at Large, CC Past-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
Statuary Cowrie Container, Western Han Dynasty (206 B.C. – A.D. 8). Excavated at Jinning, Yunan Province, 1956; Editor at Large, CC Past-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
Chinese Art: Then and Now
Chinese art certainly has evolved since prehistory and to this solar day it is still going potent. In 1949 Mainland china became a republic and art was created in a way that celebrated various governmental structures. The types of art included paintings, posters, ceramics, woodblock prints, and diverse other propaganda-driven artwork.
Due to other conflicts during the 1900s, Chinese art was stifled in its expression, however, since the 1980s there has been a new expansion and freedom of expression for China art. In that location has been more experimentation with new modalities and techniques, as well as making art for the Chinese culture, revisiting traditional Chinese art modalities.
Chinese fine art is a continental art, it spans the whole of People's republic of china and has been a cosmos of the hearts and minds of its people. From the primeval fossil finds to the latest contemporary Chinese art, it has reached the residuum of the world in many ways, but undoubtedly has left its imprint every bit one of the biggest fine art movements in the world of art history.
Take a expect at our Chinese fine art overview webstory here!
Oft Asked Questions
When Did Chinese Art First Occur?
Chinese fine art occurred as early as the Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) dated around 7000 BCE to 1700 BCE. The history of China dates to early prehistoric times (over two one thousand thousand years) when the fossils from what is referred to as the Peking Man, or Homo erectus pekinensis, were found in northern China in the Zhoukoudian Cavern, which is in the Fangshan Commune in Beijing. Chinese art has evolved upward until the nowadays times and has adult new contemporary modalities and techniques reaching across the entire art earth.
What Are Some of the Main Forms of Chinese Art?
Calligraphy, Painting, and Poetry were some of the main forms of Chinese art. These were as well referred to as the "Three Perfections". Artists would often utilize and combine the three modalities to create artworks. Calligraphy was an important part of the Chinese art civilization equally information technology was, and is, handwriting, and with this meticulous intendance and intention goes into writing information technology. Poetry and writing verse were besides important prerequisites for sure examinations.
What Are the Characteristics of Chinese Art?
The common characteristics that give Chinese art its nature come from philosophical, religious, and cultural beliefs. Chinese culture has always valued nature and its significance. A multifariousness of subject area affair is often of natural elements, for case, leaf and plants like bamboo, flowers, creature life-like birds, as well as landscapes of mountains and rivers. Furthermore, religion and moral beliefs from Buddhism, Taoism, and Confucianism were important influencing factors to how artists created art and its underlying meaning. Additionally, the court was as well an influencing factor in how people created art and the purpose it served.
What Was Chinese Painting?
Ancient Chinese landscape painting was 1 of the primary forms of painting, and is often also described as the "highest" course of painting. Artists would depict landscapes with mountainous areas and rivers, in fact, the Chinese word for mural consists of two characters that hateful "mountains and water". Paintings were usually also created on paper, which would and so be mounted on silk. The painting was as well done like calligraphy, for example, the paintbrush was dipped in pigments of varying colors of ink. At that place were as well two techniques in Chinese paintings, namely, "Gongbi" (significant "meticulous") and "Ink and Wash". There were different types of ways paintings would be mounted, for example, scrolls in the class of mitt or hanging scrolls, fans, and album leaves.
Source: https://artincontext.org/chinese-art/
0 Response to "What Was Primary Subject Matter of Ancient Chinease Art"
Post a Comment